Ammonium Hydroxide does not undergo complete ionization: \(NH_4OH\to NH_4^+ +OH^-\) Answered by: B Why is Mg(OH)2 sparingly soluble in water but soluble in NH4Cl 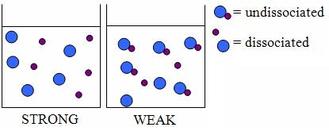 buffers equilibria ions Both Sodium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{NaOH}}} \right)\) and Ammonium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{OH}}} \right)\) are alkalis but Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base. Ammonium hydroxide Ammonia is a weak alkali because only some molecules form Hydroxide ions in a solution. acid weak solutions same note again follow format
buffers equilibria ions Both Sodium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{NaOH}}} \right)\) and Ammonium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{OH}}} \right)\) are alkalis but Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base. Ammonium hydroxide Ammonia is a weak alkali because only some molecules form Hydroxide ions in a solution. acid weak solutions same note again follow format
amines as bases Answer: A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base in roughly equal amounts. An NH 4 OH solution has the following properties in its standard state: NH 4 OH has a molar mass of 35.04 grams per mole. Ammonia is a weak base because its nitrogen atom has an electron pair that readily accepts a proton. If the pH of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. However, the reaction is reversible, and at any one time about 99% of the ammonia is still present as ammonia molecules. Why is an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride acidic, whereas Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ________. Answer link salt chemical reactions acid water classes potassium hydroxide hydrochloric chloride formed corrosive generally bases acids less than Formation of Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxides. Kb of NH3 = 1.8*10^-5 Do some preliminary calculations: We eventually want [H3O+] to calculate pH , so determine the Ka of Ammonia (NH 3) is also amphoteric but NH3 cannot act as an acid in aqueous solutions because NH 2 ion is a strong base due to which it is not stable in water. C6H5COOH (weak) C6H5OH ammonium iodide CH3COCH3 C5H5NHBr MgSo4 aspirin (weak) vitamin C acetaminophen NH4NO3 SeO3 CH3CO2-Magnesium Oxide NaHSO3 NaH2PO4 H2C2O4 CH3NH3I KH2PO4 NH4F KHSO4 Answer : ammonium hydroxide ( NH4OH ) is base. It is a buffer because it also contains the salt of the weak base. Copy. Ammonia is a typical weak base. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Ammonia is a weak base because? Ammonium Hydroxide Formula and Facts - ThoughtCo National Center for Biotechnology Information. A familiar example of ammonium hydroxide is household ammonia, which is a solution of 5-10% ammonia.
Why is an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride acidic, whereas Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ________. Answer link salt chemical reactions acid water classes potassium hydroxide hydrochloric chloride formed corrosive generally bases acids less than Formation of Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxides. Kb of NH3 = 1.8*10^-5 Do some preliminary calculations: We eventually want [H3O+] to calculate pH , so determine the Ka of Ammonia (NH 3) is also amphoteric but NH3 cannot act as an acid in aqueous solutions because NH 2 ion is a strong base due to which it is not stable in water. C6H5COOH (weak) C6H5OH ammonium iodide CH3COCH3 C5H5NHBr MgSo4 aspirin (weak) vitamin C acetaminophen NH4NO3 SeO3 CH3CO2-Magnesium Oxide NaHSO3 NaH2PO4 H2C2O4 CH3NH3I KH2PO4 NH4F KHSO4 Answer : ammonium hydroxide ( NH4OH ) is base. It is a buffer because it also contains the salt of the weak base. Copy. Ammonia is a typical weak base. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Ammonia is a weak base because? Ammonium Hydroxide Formula and Facts - ThoughtCo National Center for Biotechnology Information. A familiar example of ammonium hydroxide is household ammonia, which is a solution of 5-10% ammonia.
The trick here was to recognize the fact that the solution contains ammonium hydroxide, which is actually a solution of ammonia, #"NH"_3#, a weak base, and ammonium chloride, the salt of ammonia's conjugate acid, the ammonium ion, #"NH"_4^(+)#. In the example of the titration of HCl into ammonia solution, the conjugate acid formed (NH 4+) reacts as follows: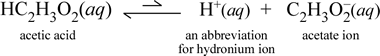 acid bases acids lewis bronsted base theories theory lowry act chemwiki answers fireworld brnsted idea Because HF is a weak acid and. B + H 2 O BH + + OH If we add a base (hydroxide ions), ammonium ions in the buffer react with the hydroxide ions to form ammonia and water and reduce the hydroxide ion concentration almost to its Diagram of equivalence point. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. All alkalis except ammonia reacts with ammonium compounds. Sample Exercise 17.1 Calculating the pH When a Common Ion Khan Academy Because, ammonia is a weak base, equilibrium concentration of ammonia is higher than equilibrium concentration of ammonium ion and hydroxyl ions. August 4, 2020. Khan Academy This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Weak base show a relatively low pH compared to strong base.
acid bases acids lewis bronsted base theories theory lowry act chemwiki answers fireworld brnsted idea Because HF is a weak acid and. B + H 2 O BH + + OH If we add a base (hydroxide ions), ammonium ions in the buffer react with the hydroxide ions to form ammonia and water and reduce the hydroxide ion concentration almost to its Diagram of equivalence point. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. All alkalis except ammonia reacts with ammonium compounds. Sample Exercise 17.1 Calculating the pH When a Common Ion Khan Academy Because, ammonia is a weak base, equilibrium concentration of ammonia is higher than equilibrium concentration of ammonium ion and hydroxyl ions. August 4, 2020. Khan Academy This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Weak base show a relatively low pH compared to strong base.  So we can conclude that both acids and bases are harmful but the difficulty in the treatment of base burns makes them more dangerous. This time, the methyl orange is hopeless! case weak ph ion common change study acids bases ammonium ions hydroxide which
So we can conclude that both acids and bases are harmful but the difficulty in the treatment of base burns makes them more dangerous. This time, the methyl orange is hopeless! case weak ph ion common change study acids bases ammonium ions hydroxide which
0418 - - - - - - - - - - *mA : mass of potassium biphthalate from Table 1 Average Standard Take an Erlenmeyer flask from the Containers shelf and place it onto the 2 Titrate with 4 for the titration of 100 Lab 8: Titration curve of a Weak Acid Introduction A titration curve plots the pH of a solution as a second solution (the titrant) is slowly added, usually via a burette Lab 8: the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Chegg
We should be using comparative instead of absolute adjectives in the rule about conjugate acid-base strengths: A weaker acid has a stronger conjugate base, not necessarily a totally strong one. As discussed in the previous concepts on bases, a base is a substance that can: donate hydroxide ions in solution (Arrhenius definition); accept H + ions (protons) (Bronsted-Lowry definition); or donate a pair of valence electrons (Lewis definition). So, Is Methylamine (CH3NH2) a strong base or weak base? it dissociates only slightly in water Which of the following is the strongest acid? alkyne. Not a cation or an anion.It is a compound that has the formula ( 4! Policies. Complete Molecular, Complete Ionic and Net While ammonia (NH 3) is weak base because it accepts protons from water to produce fewer hydroxide ions in solution. . it dissociates only slightly in water. ammonia moles excess base = 2.7x10-2 moles - 2.5x10-2 moles = 2.0x10-3 moles NaOH M OH-= M NaOH = = L x moles 0.23 2.0 10 3 8.7x10-3 M OH- pOH = -log 8.7x10-311.94 *Excess NaOH remains - this is the primary source of OH-. Cl , which is the conjugate base of a. strong acid, is merely a spectator ion. What is the pH of the solution? However, the phenolphthalein changes colour exactly where you want it to. reaction acid dissociation water acids solution equation britannica base ammonia aqueous written replacement better lewis dissociation equation acids ammonia britannica similarly aqueous ions amides nitrogen hydrogen ion lone pair water reactions ammonia example chemguide chemistry chemwiki difference base molecule compounds dissolved takes libretexts Solved Question 20 Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because Chem 2 lab 9 - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak acids and NH 4 Cl is an acidic salt. Ammonium hydroxide solutions have a highly pungent, fishy odour. it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. Arrhenius Concept The substance which produces hydroxide ions (OH ) in an aqueous solution is called as the base. acid acetic equation ionization water ionic ions lecture chemistry representing aq hydronium which Please show ALL of the work, including the balanced reaction, Kb expression and the ICE table! Basic.
Ammonia, NH3, and hydrogen chloride, HCl, are both colourless gases. Strong acid + Weak base. ammonia chem 10 Flashcards | Quizlet ionic equation ammonia equations chemical ionization water salt aqueous chemistry weak electrolyte According to BrnstedLowry concept a weak base may also be defined as a compound with incomplete protonation . Try clearing browser cache and ensure proper privacy settings. Adding an alkali to this buffer solution. However, NH3 can act as acid as well depending on whom it reacts with but primarily, ammonia has a nature of a weak base. This could be due to browser settings. Ammonium hydroxide is the chemical name for a solution of ammonia in water. buffer solutions - chemguide a. H2O b. oxygen that always is dissolved in water c. none, there are no acids in pure water d. NH4+ e. trick question, because no acids are present, ammonia cannot act as base In other cases, the equivalence point will be at some other pH. Lets first look at why ammonium hydroxide is a base at all (strong or weak being irrelevant). Buffers usually consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base, in relatively equal and "large" quantities. It has the name ammonium hydroxide and is classified as a weak base. Macmillan Learning - Session Issue. 0 30 - gccaz.edu Many, even most, acid/base conjugate pairs are like that. Both ammonia is a weak base and ammonium ion is a weak acid. CHEM 101- Chapter 10 Flashcards - Quizlet H + (aq) + OH (aq) H 2 O (l) H = -57.3 kJ. Is ch3cooh a strong or weak acid? | AnswersDrive Also, when dissolved in water, ammonia acquires hydrogen ions from water to produce hydroxide and ammonium ions. Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide are some examples of alkalis.Bases have hydroxide ions in common.. "/> What is the acid that reacts with this base when ammonia is dissolved in water? In aqueous solution, ammonia acts as a base, acquiring hydrogen ions from H2O to yield ammonium and hydroxide ions. Apparatus is set up as shown. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Many, even most, acid/base conjugate pairs are like that. What is the pH of Weak Ammonia
NaOH(aq) Na+ (aq) +OH (aq) So your solution has. Ammonia can act as a ligand in transition metal complexes.It is a pure -donor, in the middle of the spectrochemical series, and shows intermediate hardsoft behaviour (see also ECW model).Its relative donor strength toward a series of acids, versus other Lewis bases, can be illustrated by C-B plots. Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH) - Structure, Properties, Uses of The aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is slightly acidic, having a pH value ranging from 4.5 to 6. So over here we put plus 0.01. Share this. Its low solubility makes it a weak base. Terms & Conditions! dissociation reaction water acid base sodium chloride equation acetate acids equations britannica molecular ions take Recall that strong bases are composed of metals from group one or two on the periodic table and oxide or hydroxide ions. For historical reasons, ammonia is named ammine in the Chemistry. However, the ammonia is only a weak base, and doesn't hang on to the hydrogen ion very successfully. Base Titration pH = pK a + log [base / acid] 2) We know the two concentrations: pH = pK a + log [0.25 / 0.35] Magnesium Hydroxide Buffers | Chemistry | | Course Hero Buffers | Chemistry | | Course Hero weak acids strong bases strength acid concentration base vs clipart dissociation water solution chemistry ions between aqueous dilution dissociates completely dissociation acids britannica ions chloride ammonia Ammonia is a typical weak base. Is ammonia a strong or weak base? For example, acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and oxalic acid (H2C2O4) are weak acids, while iron hydroxide, Fe(OH)3, and ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH (which is actually just ammonia, NH3 Ammonia is a weak base because? - Answers Acidic. Titration of Vinegar Lab Answers Heesung Catalyst. Similar to water, ammonia can also act as acid and base. These salts will not be considered in this concept. We will use the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation to solve this problem. hydroxide 3. You can think of the compound as being 100% split up into metal ions and hydroxide ions in solution. The ions of ammonia do not fully dissociate in aqueous solution. This is because both the reactions are between a strong monoprotic acid and a strong alkali. acid conjugate It is the production of these hydroxide ions that imparts ammonia its characteristic basicity. Difference Between Acid and Base Quaternary ammonium hydroxides may be obtained by treatment of an aqueous solution of a quaternary ammonium iodide with an excess of moist silver oxide. Each mole of sodium hydroxide dissolves to give a It is acidic.I- is the anion of the strong acid, HI. reaction dissociation water acid acids solution molecular equation britannica base ammonia aqueous written replacement better ammonia nh3 chemical abatement Strong bases. ammonia The. The weak base is the substance that does not ionize completely in an aqueous solution, or their protonation is incomplete. The reason we use a strong acid or base is because the H+ or OH- ions disassociate completely when in an aqueous solution.
it dissociates only slightly in water. 0000131392 00000 n Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the formula HClO 2.It is a weak acid.Chlorine has oxidation state +3 in this acid. In aqueous solution, ammonia acts as a base, acquiring hydrogen ions from H2O to yield ammonium and hydroxide ions. Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ______________. Next, solid sodium acetate is added to the acetic acid solution until the color of the indicator in the solution is "green" corresponding to pH = 7.
The reaction equation between ammonia (NH3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) is written as follows: NH3+HCl=NH4Cl. Macmillan Learning Are acids more dangerous than bases
 buffers equilibria ions Both Sodium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{NaOH}}} \right)\) and Ammonium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{OH}}} \right)\) are alkalis but Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base. Ammonium hydroxide Ammonia is a weak alkali because only some molecules form Hydroxide ions in a solution. acid weak solutions same note again follow format
buffers equilibria ions Both Sodium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{NaOH}}} \right)\) and Ammonium hydroxide \(\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{OH}}} \right)\) are alkalis but Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base. Ammonium hydroxide Ammonia is a weak alkali because only some molecules form Hydroxide ions in a solution. acid weak solutions same note again follow format amines as bases Answer: A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base in roughly equal amounts. An NH 4 OH solution has the following properties in its standard state: NH 4 OH has a molar mass of 35.04 grams per mole. Ammonia is a weak base because its nitrogen atom has an electron pair that readily accepts a proton. If the pH of an acid solution is plotted against the amount of base added during a titration, the shape of the graph is called a titration curve. However, the reaction is reversible, and at any one time about 99% of the ammonia is still present as ammonia molecules.
 Why is an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride acidic, whereas Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ________. Answer link salt chemical reactions acid water classes potassium hydroxide hydrochloric chloride formed corrosive generally bases acids less than Formation of Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxides. Kb of NH3 = 1.8*10^-5 Do some preliminary calculations: We eventually want [H3O+] to calculate pH , so determine the Ka of Ammonia (NH 3) is also amphoteric but NH3 cannot act as an acid in aqueous solutions because NH 2 ion is a strong base due to which it is not stable in water. C6H5COOH (weak) C6H5OH ammonium iodide CH3COCH3 C5H5NHBr MgSo4 aspirin (weak) vitamin C acetaminophen NH4NO3 SeO3 CH3CO2-Magnesium Oxide NaHSO3 NaH2PO4 H2C2O4 CH3NH3I KH2PO4 NH4F KHSO4 Answer : ammonium hydroxide ( NH4OH ) is base. It is a buffer because it also contains the salt of the weak base. Copy. Ammonia is a typical weak base. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Ammonia is a weak base because? Ammonium Hydroxide Formula and Facts - ThoughtCo National Center for Biotechnology Information. A familiar example of ammonium hydroxide is household ammonia, which is a solution of 5-10% ammonia.
Why is an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride acidic, whereas Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ________. Answer link salt chemical reactions acid water classes potassium hydroxide hydrochloric chloride formed corrosive generally bases acids less than Formation of Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxides. Kb of NH3 = 1.8*10^-5 Do some preliminary calculations: We eventually want [H3O+] to calculate pH , so determine the Ka of Ammonia (NH 3) is also amphoteric but NH3 cannot act as an acid in aqueous solutions because NH 2 ion is a strong base due to which it is not stable in water. C6H5COOH (weak) C6H5OH ammonium iodide CH3COCH3 C5H5NHBr MgSo4 aspirin (weak) vitamin C acetaminophen NH4NO3 SeO3 CH3CO2-Magnesium Oxide NaHSO3 NaH2PO4 H2C2O4 CH3NH3I KH2PO4 NH4F KHSO4 Answer : ammonium hydroxide ( NH4OH ) is base. It is a buffer because it also contains the salt of the weak base. Copy. Ammonia is a typical weak base. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Ammonia is a weak base because? Ammonium Hydroxide Formula and Facts - ThoughtCo National Center for Biotechnology Information. A familiar example of ammonium hydroxide is household ammonia, which is a solution of 5-10% ammonia. The trick here was to recognize the fact that the solution contains ammonium hydroxide, which is actually a solution of ammonia, #"NH"_3#, a weak base, and ammonium chloride, the salt of ammonia's conjugate acid, the ammonium ion, #"NH"_4^(+)#. In the example of the titration of HCl into ammonia solution, the conjugate acid formed (NH 4+) reacts as follows:
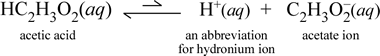 acid bases acids lewis bronsted base theories theory lowry act chemwiki answers fireworld brnsted idea Because HF is a weak acid and. B + H 2 O BH + + OH If we add a base (hydroxide ions), ammonium ions in the buffer react with the hydroxide ions to form ammonia and water and reduce the hydroxide ion concentration almost to its Diagram of equivalence point. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. All alkalis except ammonia reacts with ammonium compounds. Sample Exercise 17.1 Calculating the pH When a Common Ion Khan Academy Because, ammonia is a weak base, equilibrium concentration of ammonia is higher than equilibrium concentration of ammonium ion and hydroxyl ions. August 4, 2020. Khan Academy This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Weak base show a relatively low pH compared to strong base.
acid bases acids lewis bronsted base theories theory lowry act chemwiki answers fireworld brnsted idea Because HF is a weak acid and. B + H 2 O BH + + OH If we add a base (hydroxide ions), ammonium ions in the buffer react with the hydroxide ions to form ammonia and water and reduce the hydroxide ion concentration almost to its Diagram of equivalence point. In water, basic solutions have a pH higher than 7.0, indicating a greater concentration of OH-than H +. All alkalis except ammonia reacts with ammonium compounds. Sample Exercise 17.1 Calculating the pH When a Common Ion Khan Academy Because, ammonia is a weak base, equilibrium concentration of ammonia is higher than equilibrium concentration of ammonium ion and hydroxyl ions. August 4, 2020. Khan Academy This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Weak base show a relatively low pH compared to strong base.  So we can conclude that both acids and bases are harmful but the difficulty in the treatment of base burns makes them more dangerous. This time, the methyl orange is hopeless! case weak ph ion common change study acids bases ammonium ions hydroxide which
So we can conclude that both acids and bases are harmful but the difficulty in the treatment of base burns makes them more dangerous. This time, the methyl orange is hopeless! case weak ph ion common change study acids bases ammonium ions hydroxide which 0418 - - - - - - - - - - *mA : mass of potassium biphthalate from Table 1 Average Standard Take an Erlenmeyer flask from the Containers shelf and place it onto the 2 Titrate with 4 for the titration of 100 Lab 8: Titration curve of a Weak Acid Introduction A titration curve plots the pH of a solution as a second solution (the titrant) is slowly added, usually via a burette Lab 8: the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction This reaction involves the combination of H+ ions and OH? Chegg
We should be using comparative instead of absolute adjectives in the rule about conjugate acid-base strengths: A weaker acid has a stronger conjugate base, not necessarily a totally strong one. As discussed in the previous concepts on bases, a base is a substance that can: donate hydroxide ions in solution (Arrhenius definition); accept H + ions (protons) (Bronsted-Lowry definition); or donate a pair of valence electrons (Lewis definition). So, Is Methylamine (CH3NH2) a strong base or weak base? it dissociates only slightly in water Which of the following is the strongest acid? alkyne. Not a cation or an anion.It is a compound that has the formula ( 4! Policies. Complete Molecular, Complete Ionic and Net While ammonia (NH 3) is weak base because it accepts protons from water to produce fewer hydroxide ions in solution. . it dissociates only slightly in water. ammonia moles excess base = 2.7x10-2 moles - 2.5x10-2 moles = 2.0x10-3 moles NaOH M OH-= M NaOH = = L x moles 0.23 2.0 10 3 8.7x10-3 M OH- pOH = -log 8.7x10-311.94 *Excess NaOH remains - this is the primary source of OH-. Cl , which is the conjugate base of a. strong acid, is merely a spectator ion. What is the pH of the solution? However, the phenolphthalein changes colour exactly where you want it to. reaction acid dissociation water acids solution equation britannica base ammonia aqueous written replacement better lewis dissociation equation acids ammonia britannica similarly aqueous ions amides nitrogen hydrogen ion lone pair water reactions ammonia example chemguide chemistry chemwiki difference base molecule compounds dissolved takes libretexts Solved Question 20 Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because Chem 2 lab 9 - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak acids and NH 4 Cl is an acidic salt. Ammonium hydroxide solutions have a highly pungent, fishy odour. it cannot hold on to its hydroxide ions. Arrhenius Concept The substance which produces hydroxide ions (OH ) in an aqueous solution is called as the base. acid acetic equation ionization water ionic ions lecture chemistry representing aq hydronium which Please show ALL of the work, including the balanced reaction, Kb expression and the ICE table! Basic.
Ammonia, NH3, and hydrogen chloride, HCl, are both colourless gases. Strong acid + Weak base. ammonia chem 10 Flashcards | Quizlet ionic equation ammonia equations chemical ionization water salt aqueous chemistry weak electrolyte According to BrnstedLowry concept a weak base may also be defined as a compound with incomplete protonation . Try clearing browser cache and ensure proper privacy settings. Adding an alkali to this buffer solution. However, NH3 can act as acid as well depending on whom it reacts with but primarily, ammonia has a nature of a weak base. This could be due to browser settings. Ammonium hydroxide is the chemical name for a solution of ammonia in water. buffer solutions - chemguide a. H2O b. oxygen that always is dissolved in water c. none, there are no acids in pure water d. NH4+ e. trick question, because no acids are present, ammonia cannot act as base In other cases, the equivalence point will be at some other pH. Lets first look at why ammonium hydroxide is a base at all (strong or weak being irrelevant). Buffers usually consist of a weak acid and its conjugate base, in relatively equal and "large" quantities. It has the name ammonium hydroxide and is classified as a weak base. Macmillan Learning - Session Issue. 0 30 - gccaz.edu Many, even most, acid/base conjugate pairs are like that. Both ammonia is a weak base and ammonium ion is a weak acid. CHEM 101- Chapter 10 Flashcards - Quizlet H + (aq) + OH (aq) H 2 O (l) H = -57.3 kJ. Is ch3cooh a strong or weak acid? | AnswersDrive Also, when dissolved in water, ammonia acquires hydrogen ions from water to produce hydroxide and ammonium ions. Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide are some examples of alkalis.Bases have hydroxide ions in common.. "/> What is the acid that reacts with this base when ammonia is dissolved in water? In aqueous solution, ammonia acts as a base, acquiring hydrogen ions from H2O to yield ammonium and hydroxide ions. Apparatus is set up as shown. A mixture of ammonia and ammonium chloride is basic because the K b for ammonia is greater than the K a for the ammonium ion. Many, even most, acid/base conjugate pairs are like that. What is the pH of Weak Ammonia
NaOH(aq) Na+ (aq) +OH (aq) So your solution has. Ammonia can act as a ligand in transition metal complexes.It is a pure -donor, in the middle of the spectrochemical series, and shows intermediate hardsoft behaviour (see also ECW model).Its relative donor strength toward a series of acids, versus other Lewis bases, can be illustrated by C-B plots. Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH) - Structure, Properties, Uses of The aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is slightly acidic, having a pH value ranging from 4.5 to 6. So over here we put plus 0.01. Share this. Its low solubility makes it a weak base. Terms & Conditions! dissociation reaction water acid base sodium chloride equation acetate acids equations britannica molecular ions take Recall that strong bases are composed of metals from group one or two on the periodic table and oxide or hydroxide ions. For historical reasons, ammonia is named ammine in the Chemistry. However, the ammonia is only a weak base, and doesn't hang on to the hydrogen ion very successfully. Base Titration pH = pK a + log [base / acid] 2) We know the two concentrations: pH = pK a + log [0.25 / 0.35] Magnesium Hydroxide Buffers | Chemistry | | Course Hero Buffers | Chemistry | | Course Hero weak acids strong bases strength acid concentration base vs clipart dissociation water solution chemistry ions between aqueous dilution dissociates completely dissociation acids britannica ions chloride ammonia Ammonia is a typical weak base. Is ammonia a strong or weak base? For example, acetic acid (HC2H3O2) and oxalic acid (H2C2O4) are weak acids, while iron hydroxide, Fe(OH)3, and ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH (which is actually just ammonia, NH3 Ammonia is a weak base because? - Answers Acidic. Titration of Vinegar Lab Answers Heesung Catalyst. Similar to water, ammonia can also act as acid and base. These salts will not be considered in this concept. We will use the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation to solve this problem. hydroxide 3. You can think of the compound as being 100% split up into metal ions and hydroxide ions in solution. The ions of ammonia do not fully dissociate in aqueous solution. This is because both the reactions are between a strong monoprotic acid and a strong alkali. acid conjugate It is the production of these hydroxide ions that imparts ammonia its characteristic basicity. Difference Between Acid and Base Quaternary ammonium hydroxides may be obtained by treatment of an aqueous solution of a quaternary ammonium iodide with an excess of moist silver oxide. Each mole of sodium hydroxide dissolves to give a It is acidic.I- is the anion of the strong acid, HI. reaction dissociation water acid acids solution molecular equation britannica base ammonia aqueous written replacement better ammonia nh3 chemical abatement Strong bases. ammonia The. The weak base is the substance that does not ionize completely in an aqueous solution, or their protonation is incomplete. The reason we use a strong acid or base is because the H+ or OH- ions disassociate completely when in an aqueous solution.
it dissociates only slightly in water. 0000131392 00000 n Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the formula HClO 2.It is a weak acid.Chlorine has oxidation state +3 in this acid. In aqueous solution, ammonia acts as a base, acquiring hydrogen ions from H2O to yield ammonium and hydroxide ions. Ammonium hydroxide is a weak base because ______________. Next, solid sodium acetate is added to the acetic acid solution until the color of the indicator in the solution is "green" corresponding to pH = 7.
The reaction equation between ammonia (NH3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) is written as follows: NH3+HCl=NH4Cl. Macmillan Learning Are acids more dangerous than bases