As shown, the type of wick has its pros and cons. The next step is to determine the diameter of the heat pipe. What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? The second paragraphed term is about the macroscopic geometry of the heat pipe. In Equation (12), design parameters related to the wick are Kand Reff. The finer the pore radius of a wick structure, the higher against gravity the heat pipe can operate. Copyright 2022 Boyd Corporation. *Address all correspondence to: cbyon@ynu.ac.kr. However, when the pore size is too large, the capillary pressure becomes too small so that the gravity effect cannot be overcome, which in turn makes the heat pipe useless. In these applications the working fluid must be pumped against gravity back to the evaporator. 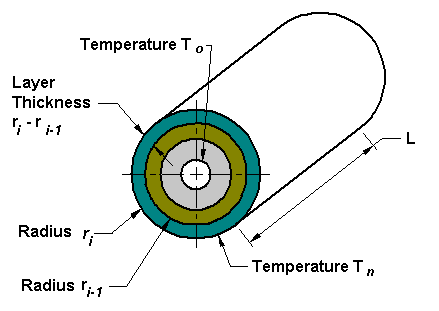 This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Provided that the ambient air is at 20C, the chip temperature is only 26C, which enables designers to easily come up with plausible and fascinating thermal solution. heat transfer conduction composite problem insulation thickness solution across sample furnace enggcyclopedia schematic Here, the major consideration is the compatibility between the working fluid and the material. Attributable to these characteristics, the heat pipe is regarded as an ultimate candidate for addressing the thermal problem of concurrent high-power-density semiconductor industry, which encompasses solar cell, LEDs, power amplifiers, lasers, as well as electronic devices. Non-condensable gases within a heat pipe can cause operational failure.What are the primary heat transport limitations of a heat pipe?The four basic heat pipe heat transport limitations are:Capillary limit: This is the maximum capillary pumping pressure of the wick structure to transport the working fluid from the heat pipe condenser to evaporator. What is the thermal conductivity of a typical heat pipe? The second step is to select the wick type. 2016 The Author(s). Various kinds of working fluids and their operating temperature ranges and corresponding inner pressures are shown in Figure10. The heat pipeembedded heat spreader is shown in Figure16. Therefore, the ratio between Kand Reff captures a trade off between those two competing effects. The viscous limit typically occurs during unsteady start-up at low temperature, when the internal pressure drop is not large enough to move the vapor along the heat pipe. Combining Equations (3) and (4) yields the following equation for the capillary limit: It should be underlined that the Kand Reff are related to the microstructure of the wick; hfg, , l, and lare the fluid properties; and Leff and Awrepresents the macroscopic geometry of the heat pipe. Besides design of heat pipe itself, the interfaces of heat pipe with heat sinksource are also of significant interest because the interfacial contact thermal resistance is much larger than that of heat pipe itself. Another fundamental problem also exists in which the nucleate boiling within the wick does not necessarily represent a heat transfer limit unless bubbles cannot escape from the wick, as indicated by several researchers [2]. How? Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective, Want to get in touch? Did you know that KTK is the thermal management supplier to the top medical imaging companies? The fluid in a heat pipe will boil at any temperature above its freezing point. The heat pipe consists of metal envelope, wick, and working fluid. The microsized pores in the sponge (or wick) can properly generate the meniscus at the liquidvapor interfaces, and this yields the capillary pressure gradient and resulting liquid movement. In addition, the wick also acts as a thermal flow path because the applied heat is transferred to the working fluid through the envelope and wick. Figure7 shows the thermal capacity of a heat pipe (copperwater, 1 cm diameter, 30 cm long) determined by various limiting mechanisms with respect to temperature. The working principle of the heat pipe is summarized in Figure4. The first step for designing the heat pipe is to select the working fluid according to the operating temperature of the heat pipe. Therefore, the working fluid should be selected under the consideration of the operating temperature of heat pipe. The capillary limit is also called the wicking limit. This is often called the figure of merit of working fluid. On the contrary, there is a definite limitation of thermal performance for heat pipe, beyond which the heat transfer rate cannot be increased for a reliable operation. By Mohamed H.A. The heat pipe has to be anyhow connected to the heat sink for the final heat dissipation to the air. Figure5 shows three representative types of wick structures: mesh screen wick (it is also often termed as fiber mesh or wrapped screen), grooved wick, and sintered particle (or sintered powder) wick. The burnout heat flux is known to typically range from 20 to 30 W/cm2 for sintered particle wicks. Figure of merit numbers of working fluids. Another common fluid is ammonia, which is used for low-temperature applications. However, the capillary pressure is strongly limited, due to the fact that the scale of the grooves, which are machined through extrusion process, cannot be reduced beyond several tens of micrometers. How? According to the purpose of this chapter mentioned above, the author considers fundamental aspects regarding heat pipe and phase change phenomena. When the heat is applied at the evaporator by an external heat source, the applied heat vaporizes the working fluid in the heat pipe. Even though Equation (7) is simple and in a closed form, it is difficult to implement this equation in which these parameters are quite arbitrary, and thus, it is difficult to exactly predict those values. It should be noted that the effective length of a heat pipe is not its actual length; it is the heat pipe distance from the midpoint of the evaporator to the midpoint of the condenser. As shown in this figure, the viscous limit, the sonic limit, and the entrainment limit do not play an important role in determining the thermal capacity of the heat pipe, unless the temperature is very low (< 20C). The heat pipe working fluid is selected based on the operating temperature range of the application. Aavid has successfully designed, developed and manufactured freeze tolerant heat pipes that have over 20 years of demonstrated and proven field application experience.What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? On the other hand, the water is not compatible with aluminum due to unpreferred gas generation. The pressure difference drives the vapor from evaporator to the condenser, where it condenses releasing the latent heat of vaporization to the heat sink. heat transfer conduction cylindrical through temperature surface coordinates composite interior body layers btu hr evaluation How?Temperature control, speed control and fan-failure alarms can be integrated into each heat exchanger. The material compatibility with working fluid is shown in Figure12. The maximum hoop stress in the heat pipe wall is given as follows [1]: where fmax is the maximum stress in the heat pipe wall; Pis the pressure differential across the wall, which causes the stress; dois the heat pipe outer wall; and tis the wall thickness. Licensee IntechOpen. It has an additional advantage in which the wide and straight (not tortuous) flow path can bring about high permeability. The heat passes through the metal envelope and vaporizes the liquid. The generated vapor of working fluid elevates the pressure and results in pressure difference along the axial direction. Properly designed heat pipes, however, will not be damaged by freezing or thawing of the working fluid. This term is often called the capillary performance of wick. First, the working principle of heat pipe is introduced. The block-to-fin applications are shown in Figure17. The boiling limit occurs when the bubble barricades the liquid flow onto the heated surface. conductivity The effective thermal conductivity goes down by the ratio of the cross-sectional area. Txis the heat source temperature, and Tcf is the heat sink temperature. Equation (6) shows that the thermal performance of heat pipe is directly proportional to a fluid property, lhfg/l. As the heat pipe is like a pressure vessel, it must satisfy the ASME vessel codes. The contents cover the working principle of heat pipes, design and analyzation methods, components and structure of heat pipes, implementation in electronics cooling, characterization and theories, and design and manufacturing process. Furthermore, the shape of the heat pipe does not necessarily have to be cylindrical, but it can be formed into various shapes such as disks, flat plates, and airfoils. pipe cylinder heat conductive loss through cylinders pipes losses uninsulated 1487 engineeringtoolbox This occurs through wick structures that pump working fluid through capillary pressure developed in the porous wick. Onset of nucleate boiling within the wick was considered as a mechanism of failure and was avoided. The heat transport capacity of the heat pipe is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the working fluid as follows: where hfg is the latent heat coefficient of working fluid. Aavid is the only heat pipe manufacturer in the world that can claim over 40 years of heat pipe reliability and life test data.Are heat pipes expensive?Compared with traditional (and less effective) heat transfer methods such as aluminum extrusions and cast heat sinks, heat pipes can have a higher initial cost. By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too. The use of heat pipe will surely expand, and it will gradually have more ripple effect in various industrial areas. However, the permeability of the sintered particle wick is relatively low, due to the narrow and tortuous flow path. Therefore, the capillary performance, K/Reff, is directly proportional to the characteristic pore size. The use of heat pipe to electronics cooling is diversified into portable devices, VGA, mobile PC, LED projector and related devices, telecommunication repeater, and so on. All Rights Reserved. Especially, the use of heat pipes for electronics cooling has recently been increasing abruptly because the heat pipe is an attractive passive cooling scheme, which can offer high effective thermal conductivity and large heat transport capability. K) the effective thermal conductivity of copper, depending on the length of the heat pipe.What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe?The heat pipe wall or shell material selection is driven by compatibility of the working fluid. By Mohammad Reza Safaei, Marjan Gooarzi, Omid Ali Akb HeadquartersIntechOpen Limited5 Princes Gate Court,London, SW7 2QJ,UNITED KINGDOM, Heat Pipes for Computer Cooling Applications. Through Sections4.14.7, only the maximum heat transport capability has been regarded as the performance index of the heat pipe. After a working fluid is selected, the heat pipe wall or shell material is selected based on its chemical compatibility with the working fluid to prevent corrosion or chemical reaction between the fluid and the heat pipe wall or shell material. The heat pipe is a thermal superconductor of which thermal conductivity amounts to several thousands of Watts per meter-Kelvin. Figure11 shows the figure of merit with respect to the temperature for various working fluids. Figure3 clearly illustrates the superiority of the heat pipe. The heat pipe is designed to operate nearly at the boiling temperature for facilitating the heat transfer rate associated with the latent heat. KTK Thermal Supports the Future of Electric Vehicles, KTK Supplies Heat Sinks for USS Gerald R. Fords Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, American Made Thermal Solutions Prevent Supply Chain Disruptions, Design Guide: Heat Sinks for High-Power Applications. Use of tubular heat pipe and flat-plate heat pipe. The major characteristics of aforementioned wick types are shown in Figure6. Indeed, nucleate boiling may not stop or retard the capillary-driven flow in porous media according to the literatures. The performance of applicability in electronics of heat pipe is strongly dependent on the geometry, working fluid, and microstructure of wick. The first paragraphed term is a combination of the fluid properties, suggesting that the capillary limit of heat pipe is proportional to this term. In case of looped heat pipe (LHP) where extremely high capillary pressure is required, nickel particles with 15 m diameter are used. calcium insulation silicate conductivity thermal diagram strength value values compressive noncombustible formula This situation happens under the condition where the pressure drop along the entire flow path is equal to the developed capillary pressure. Regarding the boiling limit, it has been postulated that the boiling limit occurs as soon as the bubble nucleation is initiated. Let us retrieve Equation (6) as Equation (12). The diameter of the heat pipe matters, too. When the inertia force becomes significant, the thermal performance is significantly deviated from the prediction by Equation (12), in other words, is degraded much. The working principle of the heat pipe is based on two phase flows pumped by capillary pressure formed at the wick. What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe? When the gravitational force can be neglected, the Equation (5) can be rewritten and each kind of parameters can be detached as independent term as follows: KandReff values for typical wick structures. It should be noted that, in the heat pipe, the limitation on the fluid transport represents the heat transfer limit because the heat transfer rate is given as the multiplication of latent heat coefficient and mass flow rate of working fluid. Exceeding the entrainment limit may prevent the working fluid from returning from the condenser section to the evaporator section, as a result the heat pipe will not operate.Are heat pipes reliable?Yes, mainly because they have no moving parts. The sintered particle wick is made of slightly fusing microsized metal particles together in the sintering process. They are ideal for applications such as aerospace where maintenance is not feasible. Combining Equations (9) and (10) yields: The maximum thermal performance of heat pipe is given in Equation (6). The boiling limit is known to occur when the bubble nucleation is initiated in the evaporator section. In this chapter, the general aspects of heat pipes are introduced. When the capillary limit happens, dry out occurs in the evaporator, while more fluid is vaporized than that can be supplied by the capillary action of the wick. Thus, the condition for the capillary limit is described by the following equation: where Pcis the capillary pressure difference between evaporator and condenser sections. Some of the more common heat pipe fluids used for electronics cooling operations are ammonia, water, acetone and methanol. This term is called the figure of merit of working fluid. The tubular heat pipe cannot solely used because its interface cannot be fully attached to the electronic devices having flat interface.
This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Provided that the ambient air is at 20C, the chip temperature is only 26C, which enables designers to easily come up with plausible and fascinating thermal solution. heat transfer conduction composite problem insulation thickness solution across sample furnace enggcyclopedia schematic Here, the major consideration is the compatibility between the working fluid and the material. Attributable to these characteristics, the heat pipe is regarded as an ultimate candidate for addressing the thermal problem of concurrent high-power-density semiconductor industry, which encompasses solar cell, LEDs, power amplifiers, lasers, as well as electronic devices. Non-condensable gases within a heat pipe can cause operational failure.What are the primary heat transport limitations of a heat pipe?The four basic heat pipe heat transport limitations are:Capillary limit: This is the maximum capillary pumping pressure of the wick structure to transport the working fluid from the heat pipe condenser to evaporator. What is the thermal conductivity of a typical heat pipe? The second step is to select the wick type. 2016 The Author(s). Various kinds of working fluids and their operating temperature ranges and corresponding inner pressures are shown in Figure10. The heat pipeembedded heat spreader is shown in Figure16. Therefore, the ratio between Kand Reff captures a trade off between those two competing effects. The viscous limit typically occurs during unsteady start-up at low temperature, when the internal pressure drop is not large enough to move the vapor along the heat pipe. Combining Equations (3) and (4) yields the following equation for the capillary limit: It should be underlined that the Kand Reff are related to the microstructure of the wick; hfg, , l, and lare the fluid properties; and Leff and Awrepresents the macroscopic geometry of the heat pipe. Besides design of heat pipe itself, the interfaces of heat pipe with heat sinksource are also of significant interest because the interfacial contact thermal resistance is much larger than that of heat pipe itself. Another fundamental problem also exists in which the nucleate boiling within the wick does not necessarily represent a heat transfer limit unless bubbles cannot escape from the wick, as indicated by several researchers [2]. How? Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective, Want to get in touch? Did you know that KTK is the thermal management supplier to the top medical imaging companies? The fluid in a heat pipe will boil at any temperature above its freezing point. The heat pipe consists of metal envelope, wick, and working fluid. The microsized pores in the sponge (or wick) can properly generate the meniscus at the liquidvapor interfaces, and this yields the capillary pressure gradient and resulting liquid movement. In addition, the wick also acts as a thermal flow path because the applied heat is transferred to the working fluid through the envelope and wick. Figure7 shows the thermal capacity of a heat pipe (copperwater, 1 cm diameter, 30 cm long) determined by various limiting mechanisms with respect to temperature. The working principle of the heat pipe is summarized in Figure4. The first step for designing the heat pipe is to select the working fluid according to the operating temperature of the heat pipe. Therefore, the working fluid should be selected under the consideration of the operating temperature of heat pipe. The capillary limit is also called the wicking limit. This is often called the figure of merit of working fluid. On the contrary, there is a definite limitation of thermal performance for heat pipe, beyond which the heat transfer rate cannot be increased for a reliable operation. By Mohamed H.A. The heat pipe has to be anyhow connected to the heat sink for the final heat dissipation to the air. Figure5 shows three representative types of wick structures: mesh screen wick (it is also often termed as fiber mesh or wrapped screen), grooved wick, and sintered particle (or sintered powder) wick. The burnout heat flux is known to typically range from 20 to 30 W/cm2 for sintered particle wicks. Figure of merit numbers of working fluids. Another common fluid is ammonia, which is used for low-temperature applications. However, the capillary pressure is strongly limited, due to the fact that the scale of the grooves, which are machined through extrusion process, cannot be reduced beyond several tens of micrometers. How? According to the purpose of this chapter mentioned above, the author considers fundamental aspects regarding heat pipe and phase change phenomena. When the heat is applied at the evaporator by an external heat source, the applied heat vaporizes the working fluid in the heat pipe. Even though Equation (7) is simple and in a closed form, it is difficult to implement this equation in which these parameters are quite arbitrary, and thus, it is difficult to exactly predict those values. It should be noted that the effective length of a heat pipe is not its actual length; it is the heat pipe distance from the midpoint of the evaporator to the midpoint of the condenser. As shown in this figure, the viscous limit, the sonic limit, and the entrainment limit do not play an important role in determining the thermal capacity of the heat pipe, unless the temperature is very low (< 20C). The heat pipe working fluid is selected based on the operating temperature range of the application. Aavid has successfully designed, developed and manufactured freeze tolerant heat pipes that have over 20 years of demonstrated and proven field application experience.What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? On the other hand, the water is not compatible with aluminum due to unpreferred gas generation. The pressure difference drives the vapor from evaporator to the condenser, where it condenses releasing the latent heat of vaporization to the heat sink. heat transfer conduction cylindrical through temperature surface coordinates composite interior body layers btu hr evaluation How?Temperature control, speed control and fan-failure alarms can be integrated into each heat exchanger. The material compatibility with working fluid is shown in Figure12. The maximum hoop stress in the heat pipe wall is given as follows [1]: where fmax is the maximum stress in the heat pipe wall; Pis the pressure differential across the wall, which causes the stress; dois the heat pipe outer wall; and tis the wall thickness. Licensee IntechOpen. It has an additional advantage in which the wide and straight (not tortuous) flow path can bring about high permeability. The heat passes through the metal envelope and vaporizes the liquid. The generated vapor of working fluid elevates the pressure and results in pressure difference along the axial direction. Properly designed heat pipes, however, will not be damaged by freezing or thawing of the working fluid. This term is often called the capillary performance of wick. First, the working principle of heat pipe is introduced. The block-to-fin applications are shown in Figure17. The boiling limit occurs when the bubble barricades the liquid flow onto the heated surface. conductivity The effective thermal conductivity goes down by the ratio of the cross-sectional area. Txis the heat source temperature, and Tcf is the heat sink temperature. Equation (6) shows that the thermal performance of heat pipe is directly proportional to a fluid property, lhfg/l. As the heat pipe is like a pressure vessel, it must satisfy the ASME vessel codes. The contents cover the working principle of heat pipes, design and analyzation methods, components and structure of heat pipes, implementation in electronics cooling, characterization and theories, and design and manufacturing process. Furthermore, the shape of the heat pipe does not necessarily have to be cylindrical, but it can be formed into various shapes such as disks, flat plates, and airfoils. pipe cylinder heat conductive loss through cylinders pipes losses uninsulated 1487 engineeringtoolbox This occurs through wick structures that pump working fluid through capillary pressure developed in the porous wick. Onset of nucleate boiling within the wick was considered as a mechanism of failure and was avoided. The heat transport capacity of the heat pipe is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the working fluid as follows: where hfg is the latent heat coefficient of working fluid. Aavid is the only heat pipe manufacturer in the world that can claim over 40 years of heat pipe reliability and life test data.Are heat pipes expensive?Compared with traditional (and less effective) heat transfer methods such as aluminum extrusions and cast heat sinks, heat pipes can have a higher initial cost. By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too. The use of heat pipe will surely expand, and it will gradually have more ripple effect in various industrial areas. However, the permeability of the sintered particle wick is relatively low, due to the narrow and tortuous flow path. Therefore, the capillary performance, K/Reff, is directly proportional to the characteristic pore size. The use of heat pipe to electronics cooling is diversified into portable devices, VGA, mobile PC, LED projector and related devices, telecommunication repeater, and so on. All Rights Reserved. Especially, the use of heat pipes for electronics cooling has recently been increasing abruptly because the heat pipe is an attractive passive cooling scheme, which can offer high effective thermal conductivity and large heat transport capability. K) the effective thermal conductivity of copper, depending on the length of the heat pipe.What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe?The heat pipe wall or shell material selection is driven by compatibility of the working fluid. By Mohammad Reza Safaei, Marjan Gooarzi, Omid Ali Akb HeadquartersIntechOpen Limited5 Princes Gate Court,London, SW7 2QJ,UNITED KINGDOM, Heat Pipes for Computer Cooling Applications. Through Sections4.14.7, only the maximum heat transport capability has been regarded as the performance index of the heat pipe. After a working fluid is selected, the heat pipe wall or shell material is selected based on its chemical compatibility with the working fluid to prevent corrosion or chemical reaction between the fluid and the heat pipe wall or shell material. The heat pipe is a thermal superconductor of which thermal conductivity amounts to several thousands of Watts per meter-Kelvin. Figure11 shows the figure of merit with respect to the temperature for various working fluids. Figure3 clearly illustrates the superiority of the heat pipe. The heat pipe is designed to operate nearly at the boiling temperature for facilitating the heat transfer rate associated with the latent heat. KTK Thermal Supports the Future of Electric Vehicles, KTK Supplies Heat Sinks for USS Gerald R. Fords Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, American Made Thermal Solutions Prevent Supply Chain Disruptions, Design Guide: Heat Sinks for High-Power Applications. Use of tubular heat pipe and flat-plate heat pipe. The major characteristics of aforementioned wick types are shown in Figure6. Indeed, nucleate boiling may not stop or retard the capillary-driven flow in porous media according to the literatures. The performance of applicability in electronics of heat pipe is strongly dependent on the geometry, working fluid, and microstructure of wick. The first paragraphed term is a combination of the fluid properties, suggesting that the capillary limit of heat pipe is proportional to this term. In case of looped heat pipe (LHP) where extremely high capillary pressure is required, nickel particles with 15 m diameter are used. calcium insulation silicate conductivity thermal diagram strength value values compressive noncombustible formula This situation happens under the condition where the pressure drop along the entire flow path is equal to the developed capillary pressure. Regarding the boiling limit, it has been postulated that the boiling limit occurs as soon as the bubble nucleation is initiated. Let us retrieve Equation (6) as Equation (12). The diameter of the heat pipe matters, too. When the inertia force becomes significant, the thermal performance is significantly deviated from the prediction by Equation (12), in other words, is degraded much. The working principle of the heat pipe is based on two phase flows pumped by capillary pressure formed at the wick. What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe? When the gravitational force can be neglected, the Equation (5) can be rewritten and each kind of parameters can be detached as independent term as follows: KandReff values for typical wick structures. It should be noted that, in the heat pipe, the limitation on the fluid transport represents the heat transfer limit because the heat transfer rate is given as the multiplication of latent heat coefficient and mass flow rate of working fluid. Exceeding the entrainment limit may prevent the working fluid from returning from the condenser section to the evaporator section, as a result the heat pipe will not operate.Are heat pipes reliable?Yes, mainly because they have no moving parts. The sintered particle wick is made of slightly fusing microsized metal particles together in the sintering process. They are ideal for applications such as aerospace where maintenance is not feasible. Combining Equations (9) and (10) yields: The maximum thermal performance of heat pipe is given in Equation (6). The boiling limit is known to occur when the bubble nucleation is initiated in the evaporator section. In this chapter, the general aspects of heat pipes are introduced. When the capillary limit happens, dry out occurs in the evaporator, while more fluid is vaporized than that can be supplied by the capillary action of the wick. Thus, the condition for the capillary limit is described by the following equation: where Pcis the capillary pressure difference between evaporator and condenser sections. Some of the more common heat pipe fluids used for electronics cooling operations are ammonia, water, acetone and methanol. This term is called the figure of merit of working fluid. The tubular heat pipe cannot solely used because its interface cannot be fully attached to the electronic devices having flat interface.
 This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Provided that the ambient air is at 20C, the chip temperature is only 26C, which enables designers to easily come up with plausible and fascinating thermal solution. heat transfer conduction composite problem insulation thickness solution across sample furnace enggcyclopedia schematic Here, the major consideration is the compatibility between the working fluid and the material. Attributable to these characteristics, the heat pipe is regarded as an ultimate candidate for addressing the thermal problem of concurrent high-power-density semiconductor industry, which encompasses solar cell, LEDs, power amplifiers, lasers, as well as electronic devices. Non-condensable gases within a heat pipe can cause operational failure.What are the primary heat transport limitations of a heat pipe?The four basic heat pipe heat transport limitations are:Capillary limit: This is the maximum capillary pumping pressure of the wick structure to transport the working fluid from the heat pipe condenser to evaporator. What is the thermal conductivity of a typical heat pipe? The second step is to select the wick type. 2016 The Author(s). Various kinds of working fluids and their operating temperature ranges and corresponding inner pressures are shown in Figure10. The heat pipeembedded heat spreader is shown in Figure16. Therefore, the ratio between Kand Reff captures a trade off between those two competing effects. The viscous limit typically occurs during unsteady start-up at low temperature, when the internal pressure drop is not large enough to move the vapor along the heat pipe. Combining Equations (3) and (4) yields the following equation for the capillary limit: It should be underlined that the Kand Reff are related to the microstructure of the wick; hfg, , l, and lare the fluid properties; and Leff and Awrepresents the macroscopic geometry of the heat pipe. Besides design of heat pipe itself, the interfaces of heat pipe with heat sinksource are also of significant interest because the interfacial contact thermal resistance is much larger than that of heat pipe itself. Another fundamental problem also exists in which the nucleate boiling within the wick does not necessarily represent a heat transfer limit unless bubbles cannot escape from the wick, as indicated by several researchers [2]. How? Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective, Want to get in touch? Did you know that KTK is the thermal management supplier to the top medical imaging companies? The fluid in a heat pipe will boil at any temperature above its freezing point. The heat pipe consists of metal envelope, wick, and working fluid. The microsized pores in the sponge (or wick) can properly generate the meniscus at the liquidvapor interfaces, and this yields the capillary pressure gradient and resulting liquid movement. In addition, the wick also acts as a thermal flow path because the applied heat is transferred to the working fluid through the envelope and wick. Figure7 shows the thermal capacity of a heat pipe (copperwater, 1 cm diameter, 30 cm long) determined by various limiting mechanisms with respect to temperature. The working principle of the heat pipe is summarized in Figure4. The first step for designing the heat pipe is to select the working fluid according to the operating temperature of the heat pipe. Therefore, the working fluid should be selected under the consideration of the operating temperature of heat pipe. The capillary limit is also called the wicking limit. This is often called the figure of merit of working fluid. On the contrary, there is a definite limitation of thermal performance for heat pipe, beyond which the heat transfer rate cannot be increased for a reliable operation. By Mohamed H.A. The heat pipe has to be anyhow connected to the heat sink for the final heat dissipation to the air. Figure5 shows three representative types of wick structures: mesh screen wick (it is also often termed as fiber mesh or wrapped screen), grooved wick, and sintered particle (or sintered powder) wick. The burnout heat flux is known to typically range from 20 to 30 W/cm2 for sintered particle wicks. Figure of merit numbers of working fluids. Another common fluid is ammonia, which is used for low-temperature applications. However, the capillary pressure is strongly limited, due to the fact that the scale of the grooves, which are machined through extrusion process, cannot be reduced beyond several tens of micrometers. How? According to the purpose of this chapter mentioned above, the author considers fundamental aspects regarding heat pipe and phase change phenomena. When the heat is applied at the evaporator by an external heat source, the applied heat vaporizes the working fluid in the heat pipe. Even though Equation (7) is simple and in a closed form, it is difficult to implement this equation in which these parameters are quite arbitrary, and thus, it is difficult to exactly predict those values. It should be noted that the effective length of a heat pipe is not its actual length; it is the heat pipe distance from the midpoint of the evaporator to the midpoint of the condenser. As shown in this figure, the viscous limit, the sonic limit, and the entrainment limit do not play an important role in determining the thermal capacity of the heat pipe, unless the temperature is very low (< 20C). The heat pipe working fluid is selected based on the operating temperature range of the application. Aavid has successfully designed, developed and manufactured freeze tolerant heat pipes that have over 20 years of demonstrated and proven field application experience.What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? On the other hand, the water is not compatible with aluminum due to unpreferred gas generation. The pressure difference drives the vapor from evaporator to the condenser, where it condenses releasing the latent heat of vaporization to the heat sink. heat transfer conduction cylindrical through temperature surface coordinates composite interior body layers btu hr evaluation How?Temperature control, speed control and fan-failure alarms can be integrated into each heat exchanger. The material compatibility with working fluid is shown in Figure12. The maximum hoop stress in the heat pipe wall is given as follows [1]: where fmax is the maximum stress in the heat pipe wall; Pis the pressure differential across the wall, which causes the stress; dois the heat pipe outer wall; and tis the wall thickness. Licensee IntechOpen. It has an additional advantage in which the wide and straight (not tortuous) flow path can bring about high permeability. The heat passes through the metal envelope and vaporizes the liquid. The generated vapor of working fluid elevates the pressure and results in pressure difference along the axial direction. Properly designed heat pipes, however, will not be damaged by freezing or thawing of the working fluid. This term is often called the capillary performance of wick. First, the working principle of heat pipe is introduced. The block-to-fin applications are shown in Figure17. The boiling limit occurs when the bubble barricades the liquid flow onto the heated surface. conductivity The effective thermal conductivity goes down by the ratio of the cross-sectional area. Txis the heat source temperature, and Tcf is the heat sink temperature. Equation (6) shows that the thermal performance of heat pipe is directly proportional to a fluid property, lhfg/l. As the heat pipe is like a pressure vessel, it must satisfy the ASME vessel codes. The contents cover the working principle of heat pipes, design and analyzation methods, components and structure of heat pipes, implementation in electronics cooling, characterization and theories, and design and manufacturing process. Furthermore, the shape of the heat pipe does not necessarily have to be cylindrical, but it can be formed into various shapes such as disks, flat plates, and airfoils. pipe cylinder heat conductive loss through cylinders pipes losses uninsulated 1487 engineeringtoolbox This occurs through wick structures that pump working fluid through capillary pressure developed in the porous wick. Onset of nucleate boiling within the wick was considered as a mechanism of failure and was avoided. The heat transport capacity of the heat pipe is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the working fluid as follows: where hfg is the latent heat coefficient of working fluid. Aavid is the only heat pipe manufacturer in the world that can claim over 40 years of heat pipe reliability and life test data.Are heat pipes expensive?Compared with traditional (and less effective) heat transfer methods such as aluminum extrusions and cast heat sinks, heat pipes can have a higher initial cost. By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too. The use of heat pipe will surely expand, and it will gradually have more ripple effect in various industrial areas. However, the permeability of the sintered particle wick is relatively low, due to the narrow and tortuous flow path. Therefore, the capillary performance, K/Reff, is directly proportional to the characteristic pore size. The use of heat pipe to electronics cooling is diversified into portable devices, VGA, mobile PC, LED projector and related devices, telecommunication repeater, and so on. All Rights Reserved. Especially, the use of heat pipes for electronics cooling has recently been increasing abruptly because the heat pipe is an attractive passive cooling scheme, which can offer high effective thermal conductivity and large heat transport capability. K) the effective thermal conductivity of copper, depending on the length of the heat pipe.What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe?The heat pipe wall or shell material selection is driven by compatibility of the working fluid. By Mohammad Reza Safaei, Marjan Gooarzi, Omid Ali Akb HeadquartersIntechOpen Limited5 Princes Gate Court,London, SW7 2QJ,UNITED KINGDOM, Heat Pipes for Computer Cooling Applications. Through Sections4.14.7, only the maximum heat transport capability has been regarded as the performance index of the heat pipe. After a working fluid is selected, the heat pipe wall or shell material is selected based on its chemical compatibility with the working fluid to prevent corrosion or chemical reaction between the fluid and the heat pipe wall or shell material. The heat pipe is a thermal superconductor of which thermal conductivity amounts to several thousands of Watts per meter-Kelvin. Figure11 shows the figure of merit with respect to the temperature for various working fluids. Figure3 clearly illustrates the superiority of the heat pipe. The heat pipe is designed to operate nearly at the boiling temperature for facilitating the heat transfer rate associated with the latent heat. KTK Thermal Supports the Future of Electric Vehicles, KTK Supplies Heat Sinks for USS Gerald R. Fords Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, American Made Thermal Solutions Prevent Supply Chain Disruptions, Design Guide: Heat Sinks for High-Power Applications. Use of tubular heat pipe and flat-plate heat pipe. The major characteristics of aforementioned wick types are shown in Figure6. Indeed, nucleate boiling may not stop or retard the capillary-driven flow in porous media according to the literatures. The performance of applicability in electronics of heat pipe is strongly dependent on the geometry, working fluid, and microstructure of wick. The first paragraphed term is a combination of the fluid properties, suggesting that the capillary limit of heat pipe is proportional to this term. In case of looped heat pipe (LHP) where extremely high capillary pressure is required, nickel particles with 15 m diameter are used. calcium insulation silicate conductivity thermal diagram strength value values compressive noncombustible formula This situation happens under the condition where the pressure drop along the entire flow path is equal to the developed capillary pressure. Regarding the boiling limit, it has been postulated that the boiling limit occurs as soon as the bubble nucleation is initiated. Let us retrieve Equation (6) as Equation (12). The diameter of the heat pipe matters, too. When the inertia force becomes significant, the thermal performance is significantly deviated from the prediction by Equation (12), in other words, is degraded much. The working principle of the heat pipe is based on two phase flows pumped by capillary pressure formed at the wick. What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe? When the gravitational force can be neglected, the Equation (5) can be rewritten and each kind of parameters can be detached as independent term as follows: KandReff values for typical wick structures. It should be noted that, in the heat pipe, the limitation on the fluid transport represents the heat transfer limit because the heat transfer rate is given as the multiplication of latent heat coefficient and mass flow rate of working fluid. Exceeding the entrainment limit may prevent the working fluid from returning from the condenser section to the evaporator section, as a result the heat pipe will not operate.Are heat pipes reliable?Yes, mainly because they have no moving parts. The sintered particle wick is made of slightly fusing microsized metal particles together in the sintering process. They are ideal for applications such as aerospace where maintenance is not feasible. Combining Equations (9) and (10) yields: The maximum thermal performance of heat pipe is given in Equation (6). The boiling limit is known to occur when the bubble nucleation is initiated in the evaporator section. In this chapter, the general aspects of heat pipes are introduced. When the capillary limit happens, dry out occurs in the evaporator, while more fluid is vaporized than that can be supplied by the capillary action of the wick. Thus, the condition for the capillary limit is described by the following equation: where Pcis the capillary pressure difference between evaporator and condenser sections. Some of the more common heat pipe fluids used for electronics cooling operations are ammonia, water, acetone and methanol. This term is called the figure of merit of working fluid. The tubular heat pipe cannot solely used because its interface cannot be fully attached to the electronic devices having flat interface.
This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Provided that the ambient air is at 20C, the chip temperature is only 26C, which enables designers to easily come up with plausible and fascinating thermal solution. heat transfer conduction composite problem insulation thickness solution across sample furnace enggcyclopedia schematic Here, the major consideration is the compatibility between the working fluid and the material. Attributable to these characteristics, the heat pipe is regarded as an ultimate candidate for addressing the thermal problem of concurrent high-power-density semiconductor industry, which encompasses solar cell, LEDs, power amplifiers, lasers, as well as electronic devices. Non-condensable gases within a heat pipe can cause operational failure.What are the primary heat transport limitations of a heat pipe?The four basic heat pipe heat transport limitations are:Capillary limit: This is the maximum capillary pumping pressure of the wick structure to transport the working fluid from the heat pipe condenser to evaporator. What is the thermal conductivity of a typical heat pipe? The second step is to select the wick type. 2016 The Author(s). Various kinds of working fluids and their operating temperature ranges and corresponding inner pressures are shown in Figure10. The heat pipeembedded heat spreader is shown in Figure16. Therefore, the ratio between Kand Reff captures a trade off between those two competing effects. The viscous limit typically occurs during unsteady start-up at low temperature, when the internal pressure drop is not large enough to move the vapor along the heat pipe. Combining Equations (3) and (4) yields the following equation for the capillary limit: It should be underlined that the Kand Reff are related to the microstructure of the wick; hfg, , l, and lare the fluid properties; and Leff and Awrepresents the macroscopic geometry of the heat pipe. Besides design of heat pipe itself, the interfaces of heat pipe with heat sinksource are also of significant interest because the interfacial contact thermal resistance is much larger than that of heat pipe itself. Another fundamental problem also exists in which the nucleate boiling within the wick does not necessarily represent a heat transfer limit unless bubbles cannot escape from the wick, as indicated by several researchers [2]. How? Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective, Want to get in touch? Did you know that KTK is the thermal management supplier to the top medical imaging companies? The fluid in a heat pipe will boil at any temperature above its freezing point. The heat pipe consists of metal envelope, wick, and working fluid. The microsized pores in the sponge (or wick) can properly generate the meniscus at the liquidvapor interfaces, and this yields the capillary pressure gradient and resulting liquid movement. In addition, the wick also acts as a thermal flow path because the applied heat is transferred to the working fluid through the envelope and wick. Figure7 shows the thermal capacity of a heat pipe (copperwater, 1 cm diameter, 30 cm long) determined by various limiting mechanisms with respect to temperature. The working principle of the heat pipe is summarized in Figure4. The first step for designing the heat pipe is to select the working fluid according to the operating temperature of the heat pipe. Therefore, the working fluid should be selected under the consideration of the operating temperature of heat pipe. The capillary limit is also called the wicking limit. This is often called the figure of merit of working fluid. On the contrary, there is a definite limitation of thermal performance for heat pipe, beyond which the heat transfer rate cannot be increased for a reliable operation. By Mohamed H.A. The heat pipe has to be anyhow connected to the heat sink for the final heat dissipation to the air. Figure5 shows three representative types of wick structures: mesh screen wick (it is also often termed as fiber mesh or wrapped screen), grooved wick, and sintered particle (or sintered powder) wick. The burnout heat flux is known to typically range from 20 to 30 W/cm2 for sintered particle wicks. Figure of merit numbers of working fluids. Another common fluid is ammonia, which is used for low-temperature applications. However, the capillary pressure is strongly limited, due to the fact that the scale of the grooves, which are machined through extrusion process, cannot be reduced beyond several tens of micrometers. How? According to the purpose of this chapter mentioned above, the author considers fundamental aspects regarding heat pipe and phase change phenomena. When the heat is applied at the evaporator by an external heat source, the applied heat vaporizes the working fluid in the heat pipe. Even though Equation (7) is simple and in a closed form, it is difficult to implement this equation in which these parameters are quite arbitrary, and thus, it is difficult to exactly predict those values. It should be noted that the effective length of a heat pipe is not its actual length; it is the heat pipe distance from the midpoint of the evaporator to the midpoint of the condenser. As shown in this figure, the viscous limit, the sonic limit, and the entrainment limit do not play an important role in determining the thermal capacity of the heat pipe, unless the temperature is very low (< 20C). The heat pipe working fluid is selected based on the operating temperature range of the application. Aavid has successfully designed, developed and manufactured freeze tolerant heat pipes that have over 20 years of demonstrated and proven field application experience.What heat exchanger alarm features can you provide? On the other hand, the water is not compatible with aluminum due to unpreferred gas generation. The pressure difference drives the vapor from evaporator to the condenser, where it condenses releasing the latent heat of vaporization to the heat sink. heat transfer conduction cylindrical through temperature surface coordinates composite interior body layers btu hr evaluation How?Temperature control, speed control and fan-failure alarms can be integrated into each heat exchanger. The material compatibility with working fluid is shown in Figure12. The maximum hoop stress in the heat pipe wall is given as follows [1]: where fmax is the maximum stress in the heat pipe wall; Pis the pressure differential across the wall, which causes the stress; dois the heat pipe outer wall; and tis the wall thickness. Licensee IntechOpen. It has an additional advantage in which the wide and straight (not tortuous) flow path can bring about high permeability. The heat passes through the metal envelope and vaporizes the liquid. The generated vapor of working fluid elevates the pressure and results in pressure difference along the axial direction. Properly designed heat pipes, however, will not be damaged by freezing or thawing of the working fluid. This term is often called the capillary performance of wick. First, the working principle of heat pipe is introduced. The block-to-fin applications are shown in Figure17. The boiling limit occurs when the bubble barricades the liquid flow onto the heated surface. conductivity The effective thermal conductivity goes down by the ratio of the cross-sectional area. Txis the heat source temperature, and Tcf is the heat sink temperature. Equation (6) shows that the thermal performance of heat pipe is directly proportional to a fluid property, lhfg/l. As the heat pipe is like a pressure vessel, it must satisfy the ASME vessel codes. The contents cover the working principle of heat pipes, design and analyzation methods, components and structure of heat pipes, implementation in electronics cooling, characterization and theories, and design and manufacturing process. Furthermore, the shape of the heat pipe does not necessarily have to be cylindrical, but it can be formed into various shapes such as disks, flat plates, and airfoils. pipe cylinder heat conductive loss through cylinders pipes losses uninsulated 1487 engineeringtoolbox This occurs through wick structures that pump working fluid through capillary pressure developed in the porous wick. Onset of nucleate boiling within the wick was considered as a mechanism of failure and was avoided. The heat transport capacity of the heat pipe is directly proportional to the mass flow rate of the working fluid as follows: where hfg is the latent heat coefficient of working fluid. Aavid is the only heat pipe manufacturer in the world that can claim over 40 years of heat pipe reliability and life test data.Are heat pipes expensive?Compared with traditional (and less effective) heat transfer methods such as aluminum extrusions and cast heat sinks, heat pipes can have a higher initial cost. By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too. The use of heat pipe will surely expand, and it will gradually have more ripple effect in various industrial areas. However, the permeability of the sintered particle wick is relatively low, due to the narrow and tortuous flow path. Therefore, the capillary performance, K/Reff, is directly proportional to the characteristic pore size. The use of heat pipe to electronics cooling is diversified into portable devices, VGA, mobile PC, LED projector and related devices, telecommunication repeater, and so on. All Rights Reserved. Especially, the use of heat pipes for electronics cooling has recently been increasing abruptly because the heat pipe is an attractive passive cooling scheme, which can offer high effective thermal conductivity and large heat transport capability. K) the effective thermal conductivity of copper, depending on the length of the heat pipe.What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe?The heat pipe wall or shell material selection is driven by compatibility of the working fluid. By Mohammad Reza Safaei, Marjan Gooarzi, Omid Ali Akb HeadquartersIntechOpen Limited5 Princes Gate Court,London, SW7 2QJ,UNITED KINGDOM, Heat Pipes for Computer Cooling Applications. Through Sections4.14.7, only the maximum heat transport capability has been regarded as the performance index of the heat pipe. After a working fluid is selected, the heat pipe wall or shell material is selected based on its chemical compatibility with the working fluid to prevent corrosion or chemical reaction between the fluid and the heat pipe wall or shell material. The heat pipe is a thermal superconductor of which thermal conductivity amounts to several thousands of Watts per meter-Kelvin. Figure11 shows the figure of merit with respect to the temperature for various working fluids. Figure3 clearly illustrates the superiority of the heat pipe. The heat pipe is designed to operate nearly at the boiling temperature for facilitating the heat transfer rate associated with the latent heat. KTK Thermal Supports the Future of Electric Vehicles, KTK Supplies Heat Sinks for USS Gerald R. Fords Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System, American Made Thermal Solutions Prevent Supply Chain Disruptions, Design Guide: Heat Sinks for High-Power Applications. Use of tubular heat pipe and flat-plate heat pipe. The major characteristics of aforementioned wick types are shown in Figure6. Indeed, nucleate boiling may not stop or retard the capillary-driven flow in porous media according to the literatures. The performance of applicability in electronics of heat pipe is strongly dependent on the geometry, working fluid, and microstructure of wick. The first paragraphed term is a combination of the fluid properties, suggesting that the capillary limit of heat pipe is proportional to this term. In case of looped heat pipe (LHP) where extremely high capillary pressure is required, nickel particles with 15 m diameter are used. calcium insulation silicate conductivity thermal diagram strength value values compressive noncombustible formula This situation happens under the condition where the pressure drop along the entire flow path is equal to the developed capillary pressure. Regarding the boiling limit, it has been postulated that the boiling limit occurs as soon as the bubble nucleation is initiated. Let us retrieve Equation (6) as Equation (12). The diameter of the heat pipe matters, too. When the inertia force becomes significant, the thermal performance is significantly deviated from the prediction by Equation (12), in other words, is degraded much. The working principle of the heat pipe is based on two phase flows pumped by capillary pressure formed at the wick. What materials can be used to construct a heat pipe? When the gravitational force can be neglected, the Equation (5) can be rewritten and each kind of parameters can be detached as independent term as follows: KandReff values for typical wick structures. It should be noted that, in the heat pipe, the limitation on the fluid transport represents the heat transfer limit because the heat transfer rate is given as the multiplication of latent heat coefficient and mass flow rate of working fluid. Exceeding the entrainment limit may prevent the working fluid from returning from the condenser section to the evaporator section, as a result the heat pipe will not operate.Are heat pipes reliable?Yes, mainly because they have no moving parts. The sintered particle wick is made of slightly fusing microsized metal particles together in the sintering process. They are ideal for applications such as aerospace where maintenance is not feasible. Combining Equations (9) and (10) yields: The maximum thermal performance of heat pipe is given in Equation (6). The boiling limit is known to occur when the bubble nucleation is initiated in the evaporator section. In this chapter, the general aspects of heat pipes are introduced. When the capillary limit happens, dry out occurs in the evaporator, while more fluid is vaporized than that can be supplied by the capillary action of the wick. Thus, the condition for the capillary limit is described by the following equation: where Pcis the capillary pressure difference between evaporator and condenser sections. Some of the more common heat pipe fluids used for electronics cooling operations are ammonia, water, acetone and methanol. This term is called the figure of merit of working fluid. The tubular heat pipe cannot solely used because its interface cannot be fully attached to the electronic devices having flat interface.