Solubility in water. 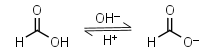 : 2: Set the UV monitor to an appropriate wavelength for your molecule. When the buffer has a pH below the protein pI, the protein will have a positive net charge and bind to a negatively charged support or cation exchange medium. Throughout this paper protein L refers to the Y43W point mutant of protein L . where: R f = relative mobility, normalized to the dye front or some other standard. In addition, protein have side chains, many of them can be protonated/deprotonated, they can serve as pH buffer. This wide range is due to phosphoric acid having 3 dissociation constants, (known in chemistry as a triprotic acid) allowing for formulation of buffers near each of the pH levels of 2.15, 6.86, or 12.32. 3) Perform the Bio-Rad RC DC protein assay: Preparation: Protein samples should be kept on ice. 17. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be applied to tell us the proportions of dihydrogen phosphate and monohydrogen phosphate present in a buffered system between pH 4 and 10. Role of Buffers in Protein Formulations - ScienceDirect K eq = [H+][OH] [H 2 O] At 25C, the concentration of pure water is 55.5 M (1000 18; M.W. Plasma Protein Binding in the ECF what does moving the bicarbonate equation to the left do? 1. For non-adherent cells, add 400 l of buffer per 107 cells once they have been washed in 1X PBS and pelleted. Biological Buffers: pH Range and How to Prepare Them
: 2: Set the UV monitor to an appropriate wavelength for your molecule. When the buffer has a pH below the protein pI, the protein will have a positive net charge and bind to a negatively charged support or cation exchange medium. Throughout this paper protein L refers to the Y43W point mutant of protein L . where: R f = relative mobility, normalized to the dye front or some other standard. In addition, protein have side chains, many of them can be protonated/deprotonated, they can serve as pH buffer. This wide range is due to phosphoric acid having 3 dissociation constants, (known in chemistry as a triprotic acid) allowing for formulation of buffers near each of the pH levels of 2.15, 6.86, or 12.32. 3) Perform the Bio-Rad RC DC protein assay: Preparation: Protein samples should be kept on ice. 17. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be applied to tell us the proportions of dihydrogen phosphate and monohydrogen phosphate present in a buffered system between pH 4 and 10. Role of Buffers in Protein Formulations - ScienceDirect K eq = [H+][OH] [H 2 O] At 25C, the concentration of pure water is 55.5 M (1000 18; M.W. Plasma Protein Binding in the ECF what does moving the bicarbonate equation to the left do? 1. For non-adherent cells, add 400 l of buffer per 107 cells once they have been washed in 1X PBS and pelleted. Biological Buffers: pH Range and How to Prepare Them 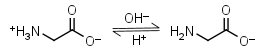
In that study, activation energy (E a) was determined using the Arrhenius equation to determine the extent to which proteins clustered and aggregated in solution. Polymers | Free Full-Text | Structural Exploration on Because TCA is an acid, the protein pellet is either washed with 75% acetone to remove the TCA, or base is added after the pellet is resuspended in SDS-PAGE sample buffer (until the bromophenol blue turns from yellow back to blue) to neutralize the pH. The formula can also be used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution or the equilibrium pH of an acid-base reaction. R = 8.314 J/(mol K) universal gas constant, Appendix 3: The common units used in biology. In free amino acids, both the main structural chain and the side chain can act as buffers. In a protein, most of the carboxylic and amino groups in the main chain are tied up in peptide bonds. In living organisms, the pH of the blood is maintained at a pH of 7.4. Chromatography and the strategy of protein purification. The total protein concentration in CSF is an indicator of bloodCSF permeability. viscosity additives buffer protein Buffer pKa and pH Range Values For preparation of .  Buffer Systems of Blood | Biochemistry - Biology Discussion Dialysis Methods for Protein Research Protein protein BUFFER SYSTEMS THAT ASSIST pH REGULATION physiological buffers When any acidic substance enters the bloodstream, the bicarbonate ions neutralize the hydronium ions forming carbonic acid and water. was filled with 1 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 0.1 M). To describe how a buffer solution (either acidic or Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Calculator How to use a protein assay standard curve - Thermo Fisher A Protein Moreover, net charge of the protein is in tight relation with the solution (buffer) pH. Physiological buffers are chemicals used by the body to prevent large changes in the "pH" of a bodily fluid. Microsolutes that are partially retained by the membrane will require additional DV. A protein is a long chain of amino acid residues, but this long chain still has free carboxylate groups COO and free amino groups NH 2. Figure 1 shows the binding curves for SpAIgG complex in both PBS-T buffer and FreeStyle 293 expression medium. It is the most important ECF buffer for metabolic acids but it cannot buffer respiratory acid-base disorders. Differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) is an accessible, rapid, and economical biophysical technique that has seen many applications over the years, ranging from protein folding state detection to the identification of ligands that bind to the target protein. (these two provided by filtration) 3. following equation. pH 6.2 (Activation buffer) PBS. Preparative HPLC System: A Definitive Fluorescence Add 3.394 g of Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate to the solution. Buffer Reference Center - Sigma-Aldrich
Buffer Systems of Blood | Biochemistry - Biology Discussion Dialysis Methods for Protein Research Protein protein BUFFER SYSTEMS THAT ASSIST pH REGULATION physiological buffers When any acidic substance enters the bloodstream, the bicarbonate ions neutralize the hydronium ions forming carbonic acid and water. was filled with 1 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 7.4, 0.1 M). To describe how a buffer solution (either acidic or Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Calculator How to use a protein assay standard curve - Thermo Fisher A Protein Moreover, net charge of the protein is in tight relation with the solution (buffer) pH. Physiological buffers are chemicals used by the body to prevent large changes in the "pH" of a bodily fluid. Microsolutes that are partially retained by the membrane will require additional DV. A protein is a long chain of amino acid residues, but this long chain still has free carboxylate groups COO and free amino groups NH 2. Figure 1 shows the binding curves for SpAIgG complex in both PBS-T buffer and FreeStyle 293 expression medium. It is the most important ECF buffer for metabolic acids but it cannot buffer respiratory acid-base disorders. Differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) is an accessible, rapid, and economical biophysical technique that has seen many applications over the years, ranging from protein folding state detection to the identification of ligands that bind to the target protein. (these two provided by filtration) 3. following equation. pH 6.2 (Activation buffer) PBS. Preparative HPLC System: A Definitive Fluorescence Add 3.394 g of Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate to the solution. Buffer Reference Center - Sigma-Aldrich